For Every Cell, For Everyday Life
Magnesium is one undoubtedly our most favourite mineral. BetterYou was founded on the principle that you cannot thrive in modern life unless you optimise you magnesium intake. Quite simply, a magnesium rich body will be stronger, more flexible and better able to deal with physical and mental stress of our modern lives.
Magnesium insufficiency is difficult to detect
Magnesium insufficiency is difficult to detect
Think of magnesium as a helper that every cell needs. It’s involved in more than 300 enzyme reactions — from making ATP (the cell’s energy currency) to building proteins, managing muscle contraction and helping DNA and RNA do their jobs.
Without enough elemental magnesium inside cells, energy production slows, cellular repair falters, and systems that rely on quick communication (like nerves and muscles) start to misfire.
Why is Magnesium so important?
Magnesium plays a fundamental role inside every cell in your body. It helps turn the food you eat into usable energy, keeps your muscles and nerves talking to each other, supports healthy sleep and mood, and even helps your cells detoxify and repair. Lots of people don’t get enough these days — thanks to modern diets, stressed-out lifestyles and other factors — so it’s worth paying attention.
Magnesium promotes better sleep
Many people use magnesium to support sleep, thanks to its ability to reduce central nervous system activity, relax muscles and reduce stress, helping people fall asleep faster and stay asleep better.
Magnesium supports memory
Are you struggling to remember things? You might need a magnesium supplement! Studies have shown that magnesium can help reduce daytime sleepiness by supporting sleep and can enhance memory.
Magnesium supports strong bones
When it comes to bone health, calcium and vitamin D tend to get most of the attention, but magnesium has its vital place, too.
Magnesium can reduce blood pressure
Hypertension is one of the most common cardiovascular diseases worldwide, and simple diet and lifestyle factors—like adding more magnesium to your diet or adding a magnesium supplement to your daily routine—can help lower blood pressure and improve cardiovascular health.
Low magnesium levels have been shown to cause sleep interruptions and
may contribute to insomnia.
They found that a magnesium supplement improved subjective measures of
insomnia, including sleep efficiency, sleep time and onset latency, early
morning awakening, and objective measures like serum renin, melatonin, and
cortisol concentrations.
It can also help promote a healthy circadian rhythm—the internal “clock”
that controls our sleep-wake cycles.
A 2010 study published in Neuron found that increasing brain magnesium levels can enhance learning abilities, working memory, and short- and long-term memory in rodents.
Adequate levels of magnesium are required for the absorption of vitamin
D and calcium, in fact calcium is insoluble without the presence of magnesium
and it is undissolved calcium which can settle in soft tissue and around joints
rather than entering the bone. Studies show that a magnesium deficiency
increases the risk of osteoporosis directly by interfering with crystal formation and on bone cells and indirectly by affecting the secretion and the activity of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and by promoting low-grade inflammation.
Studies show that, especially for people who have an existing magnesium deficiency, increasing magnesium levels can benefit high blood pressure, helping to reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. How does it do this?
There are several ways:
- Acts as a natural calcium channel blocker
- Blocks sodium from attaching to smooth muscle cells
- Increases vasodilating prostaglandin E1 (magnesium
deficiency reduces levels of PGE1 and causes vasoconstriction) - Binds potassium
- Boosts nitric oxide production
- Improves endothelial dysfunction
- Stimulates vasodilation
- Magnesium regulates blood sugar
For people that struggle to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, you
know it’s not always easy—but magnesium might be a valuable tool for helping.
Magnesium plays a vital role in regulating blood glucose and insulin
through several mechanisms, and studies have linked high magnesium diets to a
lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
Research has shown that magnesium helps the body break down sugars to
maintain healthy blood sugar levels and may reduce the risk of insulin
resistance—a precursor to diabetes.
Magnesium Supplements


Magnesium supports several detox and repair pathways:
When magnesium is low, these detox/repair systems are less efficient. Cells can become more vulnerable to oxidative stress, recover more slowly from damage, and accumulate dysfunction that contributes to tiredness, poor recovery and long-term health risks.
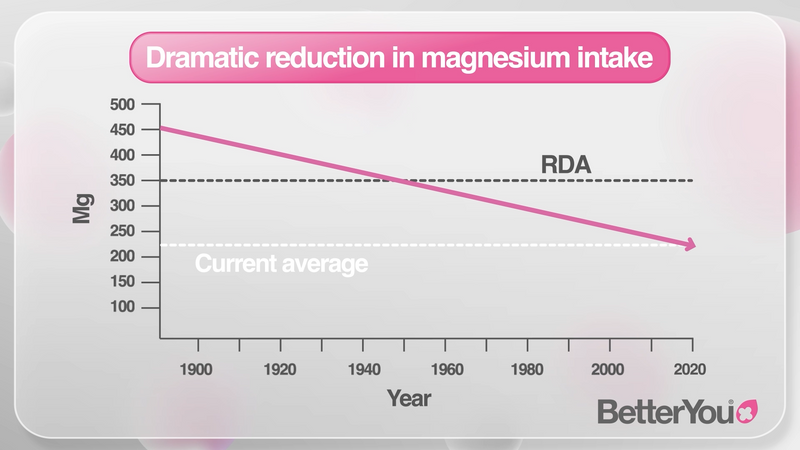
The dramatic decline in our Magnesium intake
Health authorities around the World are warning about our reduced magnesium intake. Yet, little has been done to date to rectify this.
Industrialised agriculture
Increasingly processed food
Declining digestive efficiency
Increasing prescription medication
UK
Around the world